java:user_interface_components_and_2d_graphics
Table of Contents
User Interface Components and 2D Graphics
User Interface and Interactive Components
- A good GUI API or package would allow you to …
- Create user interface components
- Customize the behavior of the components
- group and arrange the controls on the screen
- access window manager facilities (e.g., reading image files, printing, and identifying which window is focused)
- User interface (WIMP - “Window, Icon, Menu, Pointing device”):
- Window
- Buttons
- Menus
- Text boxes
- Dialog boxes
- Event handling:
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- Focus / window
- These are the essentials of writing graphics-based applications
The Java Approach
- Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT) - Native “peer” code; operating system dependent
- Not all platforms support the same widget set (some richer than others)
- Different bugs in the AWT user interface library on different platforms
- Widgets may have different behaviors on different platforms
- Swing - Consistent user experience across platforms; less dependent on underlying platform, as compared to AWT
- Many Swing components extend AWT components.
- Thus, both the AWT and Swing libraries are necessary (in most cases).
- Container - A user interface component that can contain other user interface components such as buttons and text fields
- Events
- Toolkit - Class that gets system-dependent information (e.g., getting the screen size)
The Frame
- The top level window (that is, a window that is not contained inside another window)
- JFrame (Swing)
- JFrame extends the Frame class of AWT
- Is a container
- Pertinent methods:
- setSize()
- setLocation()
- setTitle()
- setIconImage()
- setVisible()
The Panel
- JPanel
- The internal structure of a JFrame
- Is a container
- Has a surface onto which you can draw via paint() or paintComponent() methods
- Some Java game developers use Canvas (AWT) instead of JPanel (Swing)
- The difference: a JPanel can contain other components while a Canvas cannot
- paint() is used for Canvas.
- paint() can also be used in JPanel.
Swing User Interface Components
- JButton
- JTextField
- JLabel
- JCheckBox
- JRadioButton
- JComboBox
- JMenuBar
- JPasswordField
Event Handling
- Event source (the widgets): button, text box, radio button, etc.
- In response to mouse movement/click, keyboard press, etc.
- Event listener - An object to which a component has delegated the task of handling a particular kind of event
- The event source sends out event objects to all registered listeners when that event occurs.
- The listener objects will then use the information in the event object to determine their reaction to the event.
Handling Mouse Clicking Events
- MouseListener class
- MouseEvent
- Required methods:
- public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
- public void mousePressed (MouseEvent e)
- public void mouseReleased (MouseEvent e)
- public void mouseEntered (MouseEvent e)
- public void mouseExited (MouseEvent e)
Handling Keyboard Events
- Require FocusListener, KeyListener classes
- KeyEvent
- Required methods:
- public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
- public void keyTyped (KeyEvent e)
- public void keyReleased (KeyEvent e)
- public void focusGained (FocusEvent e)
- public void focusLost (FocusEvent e)
2D Graphics
Vector vs. Raster Graphics
- Vector:
- Drawings defined as lines; no curves and limited colors
- Benefits: No jagged lines (aliasing); only store endpoints of lines
- Examples: Asteroids and Battlezone
- Raster:
- Screen is made up of pixels
- Colors are defined by mixtures of 3 color sources: red, green, and blue (RGB)
- Benefits: Can easily draw solid surfaces; cheaper
- Drawbacks: More memory-intensive (but memory is cheap); aliasing problems
2D Rendering Primitives
- Point
- Line
- Polygon
- Closed (all lines connected)
- Defined by a list of vertices
Coordinate System
- Two coordinate spaces in Java
- User space - Where the graphics primitives are defined; device independent
- Device space - The coordinate system of an output device, such as a screen, window, or a printer; device dependent
- The necessary conversions between user space and device space are performed automatically during rendering
2D Graphics in Java
- Links:
- http://courses.coreservlets.com/Course-Materials/java5.html (follow “Java 2D” link)
- Uses older Graphics class but still useful:
- Graphics class
- Introduced in JDK version 1.0
- Methods to draw lines and basic shapes
- Very limited drawing options (e.g., cannot vary the line thickness; cannot rotate shapes)
- Graphics2D class
- A new type of Graphics object: Graphics2D extends Graphics
- More sophisticated control over geometry, coordinate transformations, color management, and text layout
- Supports shape manipulations
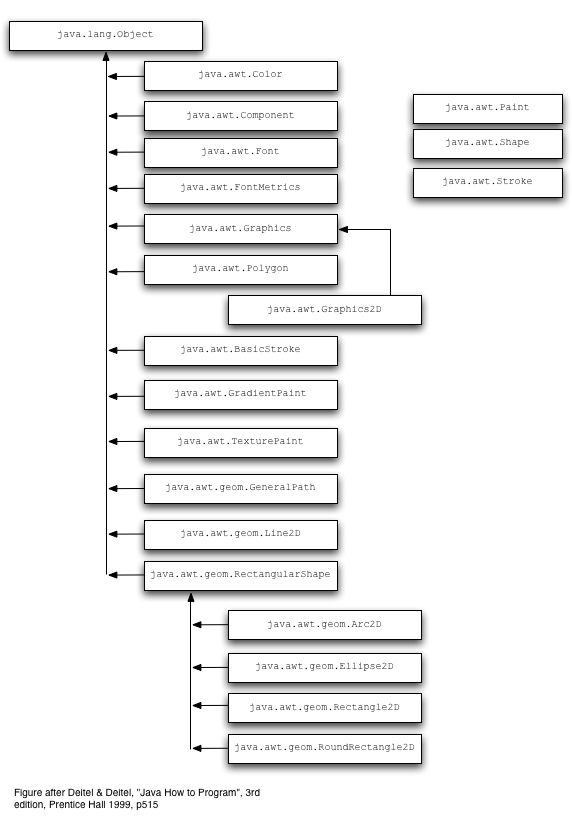
- Packages (Java 2D API)
- java.awt.*
- The main package for the Java Abstract Window Toolkit.
- java.awt.geom.*
- The Java standard library of two dimensional geometric shapes such as lines, ellipses, and quadrilaterals.
- java.awt.font.*
- The library for manipulating glyphs in Java.
- java.awt.color.*
- The library dealing with the many different ways that color can be represented.
- java.awt.image.*
- The library for manipulating graphical images.
- java.awt.print.*
- The library of tools for writing to paper.
The Java 2D paintComponent() Method in a JPanel
public void paintComponent (Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
// This is where you will do your work
...
...
}
Old Graphics Primitive Methods (That Still Work)
- drawLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
- drawRect(int x, int y, int width, int height)
- fillRect(int x, int y, int width, int height)
- drawOval(int x, int y, int width, int height)
- fillOval(int x, int y, int width, int height)
- drawString(String str, int x, int y)
- drawPolygon(int[] xPoints, int[] yPoints, int nPoints)
- fillPolygon(int[] xPoints, int[] yPoints, int nPoints)
Colors
- Use setColor() or setPaint()
- A number of standard colors in Java:
- Color.white
- Color.red
- Color.blue
- Color.cyan
- Color.green
- Or, specify your own color using RGB values
- Color(int r, int g, int b)
- Color(float r, float g, float b)
Graphics2D Primitive Methods
- Geometric shapes are organized in an object-oriented fashion
- Line2D
- Rectangle2D
- Ellipse2D
- The three classes above implement the Shape interface
- To draw a shape, create an object of a class that implements the Shape interface and then call the draw() or fill() method of the Graphics2D class.
- setStroke() - Set the line width.
- Need to create a stroke via BasicStroke()
- Rectangle2D.Double(double x, double y, double w, double h)
- Rectangle2D.Float(float x, float y, float w, float h)
- Ellipse2D.Double(double x, double y, double w, double h)
- Ellipse2D.Float(float x, float y, float w, float h)
- Point2D.Double(double x, double y)
- Line2D.Double(Point2D start, Point2D end)
- Line2D.Double(double startX, double startY, double endX, double endY)
- Arc2D.Double(double x, double y, double w, double h, double start, double extent, int type)
- Arc2D.Float(float x, float y, float w, float h, float start, float extent, int type)
- RoundRectangle2D.Double(double x, double y, double w, double h, double arcw, double arch)
- RoundRectangle2D.Float(float x, float y, float w, float h, float arcw, float arch)
Manipulations and Transformations
- translate() - Specify a translation offset in the x and y directions
- rotate() - Specify an angle of rotation in radians
- shear() - Specify a shearing factor in the x and y directions
- scale() - Specify a scaling factor in the x and y directions
Moving Pictures
- Whether it's this:
- … or this:
- After you've done your painting through paint() or paintComponent()
- Repaint:
- repaint() - Force repainting on the screen.
- repaint() causes paintComponent() to be called for all components.
Drawing Images (external images, e.g. gif, png, jpg)
- Need, at the very least, java.awt.image.* (Image class (AWT))
- drawImage(Image img, int x, int y, ImageObserver observer)
Code Samples
Lab Activity - Etch-A-Sketch (tm) emulator?
- Purpose: Utilize Java Swing, Graphics2D, and KeyListener to construct an Etch-A-Sketch ™ emulator.
- Introduction
- You are to construct an electronic version of a famous childhood toy that draws lineographic images.
- Instead of using two knobs to control the drawing stylus, the arrow keys will be moved.
- Instructions
- In Eclipse, create a new Java project “Sketch”
- Download the template Sketch.java into your project folder
- The template is partially complete with the application window / frame and key listener implemented. The drawing function(s) are left out.
- Additional
- Make holding down the shift key produce a longer line.
- Update the program so that a press of the spacebar will clear your sketch drawing.
- Update the program so it will accept key combinations to draw diagonal lines.
- For example: <up>+<right> draws a diagonal line up and to the right.
- Of course, it would be simpler to just map a single key to draw a diagonal line, but many games use a combination of the arrow keys to produce certain actions, such as jumping across obstacles.
- Links
- http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/awt/Image.html (AWT Image Class)
- http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/awt/event/InputEvent.html (handling keyboard modifiers, e.g. <shift>)
- http://math.hws.edu/eck/cs124/javanotes3/c6/s5.html (something on Java VK_ keycodes)
java/user_interface_components_and_2d_graphics.txt · Last modified: 2009/10/09 11:43 by jchung